
 Comptes Rendus Palevol
9 (6-7) - Pages 369-375
Comptes Rendus Palevol
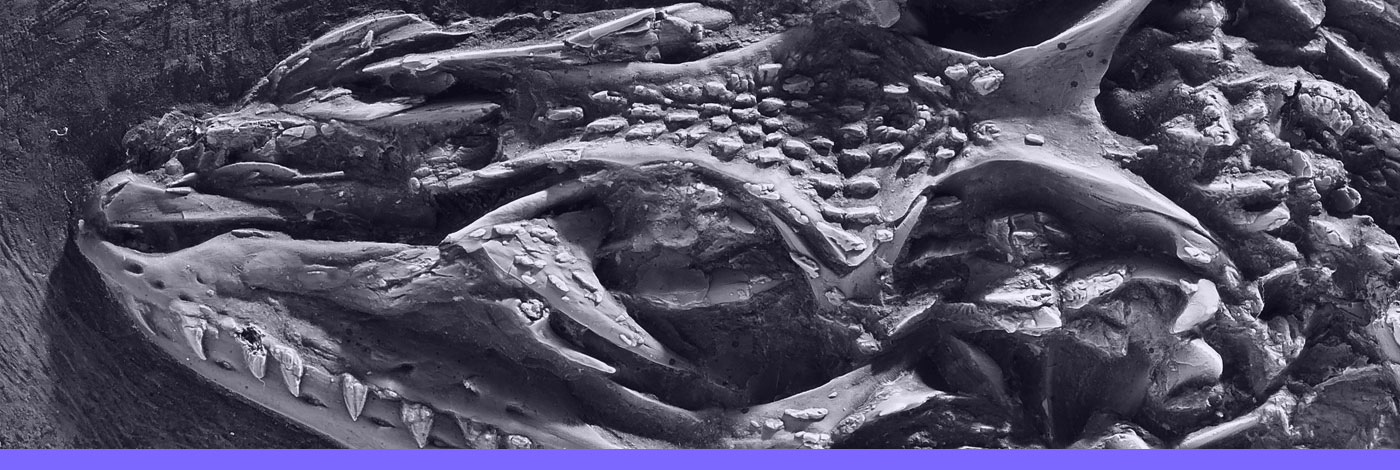
9 (6-7) - Pages 369-375The Placodermi (armored jawed fishes), which appeared during the Lower Silurian and disappeared without leading any descendants at the end of the Famennian (Latest Devonian), have the highest diversity of known Devonian vertebrate groups. As phylogenetically basal gnathostomes (jawed vertebrates), they are potentially informative about primitive jawed vertebrate anatomy and origins. Until recently, the study of their internal or histological structures has required destructive methods such as sectioning or serial grinding. Recent advances in tomography and imaging technologies, especially through the increasing use of synchrotron phase contrast imaging for the study of fossils, allow us to reveal the inner structures of the fossil nondestructively and with unprecedented three-dimensional level of detail. Here, we present for the first time the prerostral anatomy of the small acanthothoracid Romundina stellina , one of the earliest and most basal placoderms. Phase contrast imaging allows us to reconstruct the vascularization and nerve canals of the premedian plate and adjacent parts of the skeleton three-dimensionally in great detail, providing important clues to the growth modes and biology of the animal.
Bone growth, Phase contrast X-ray synchrotron Microtomography, Microanatomy, Placodermi, Vascularization