
 Comptes Rendus Palevol
4 (3) - Pages 265-274
Comptes Rendus Palevol
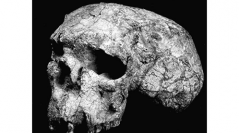
4 (3) - Pages 265-274In 1989 and 1990, two Homo erectus crania were recovered from Yunxian (Hubei province) in archaeological levels dated to more than 780 000 years. Considered along with Lantian, these skulls represent the oldest human remains discovered in China to date, constituting important palaeontological finds. Nevertheless, the crania were badly deformed during the course of fossilization, necessitating extensive cranial reconstruction. Of the two crania, only Yunxian II was in sufficient condition to carry out this reconstruction. Using sophisticated techniques only recently applied in human palaeontology, including computed tomography and rapid prototyping, and incorporating taphonomic and morphometrically-based hypotheses, we were able to correct virtually the deformation and to produce a 3D prototype of Yunxian II.
Computed tomography, Virtual anthropology, Taphonomy, Thin plate spline