
 Comptes Rendus Palevol
18 (7) - Pages 735-745
Comptes Rendus Palevol
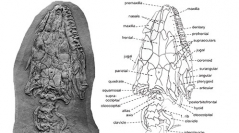
18 (7) - Pages 735-745We describe the first juvenile specimen of an eolacertid lizard. The material comes from one of the most important Eocene localities, the Messel Pit in Germany. The new specimen provides unique information on the early ontogeny of Eolacerta, the largest known lizard from Messel, with a maximum snout-vent length greater than 30 cm and a mass approaching 1 kg. The specimen described here, with a SVL of 11.3 cm and an estimated mass of 21 g, can be allocated more precisely to Eolacerta robusta based on the co-occurrence and the combination of following features: (1) the nasal process of premaxilla is long; (2) position of lacrimal (being more anteriorly located in Stefanikia siderea); (3) the postorbital process of jugal is broad; (4) the ratio of the anterior and posterior region of the frontal between the sulcus interfacialis; (5) a mid-parietal constriction of the parietal table is present; (6) the interparietal shield broadens anteriorly; (7) the transverse sulcus is straight anteriorly. The incipient character of the parietal constriction and the slightly lower number of maxillary teeth (28 vs. 30–32 in adults) are consistent with a juvenile animal. Very important is evidence for the presence of pterygoid dentition (pointed teeth arranged in a single line) and the absence of palatine dentition. Ceratobranchial I is observed for the first time for this species, and its shape and length are very similar to those of Lacertidae. There are 27 presacral vertebrae in the juvenile, as in adults. In the juvenile specimen, ventral keel on the centrum is present in all vertebrae. The ventromedial portion of the ischium is well preserved here and gives information on the exact shape of this portion, at least in juvenile form. The scalation, as far as it is preserved, is similar to that of Stefanikia , except that the rectangular subdigital scales are longer in comparison with their width, and therefore have a broader appearance.
Vertebrates, ontogeny, osteology, Palaeogene, Europe