
 Comptes Rendus Palevol
9 (6-7) - Pages 277-282
Comptes Rendus Palevol
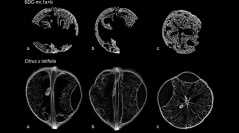
9 (6-7) - Pages 277-282The discovery of the carbonized remains of a Citrus-like fruit in a funerary offering deposit dated back to the beginning of the 6th century BC during archaeological work run at Ischia, the island which hosted one among the earliest Greek colonies in southern Italy, has relaunched the question of the spread of Citrus through western Mediterranean during Classical Antiquity. Here we apply microtomography (SR-μCT and μCT) to investigate the inner structure of the archaeological specimen (SDC-mr.1a+b). Our high-resolution comparative analysis, which also considered one carbonized modern Citrus and a dried modern Sorbus domestica (true service tree) and Malus type sylvestris (wild apple), does not support the original taxonomic attribution (
Citrus, Archaeobotany, Magna Grecia, Microtomography, Comparative analysis, Maloideae, South Italy