
 Comptes Rendus Palevol
22 (35) - Pages 711-727
Comptes Rendus Palevol
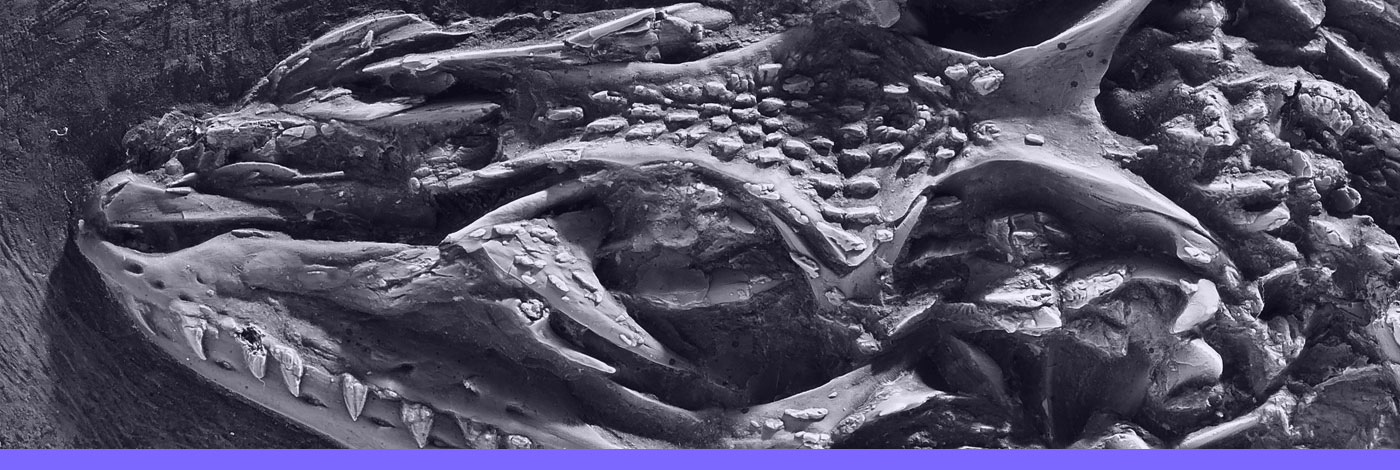
22 (35) - Pages 711-727The Eocene-Oligocene transition marks a period of dramatic global climatic change correlated with pronounced mammalian faunal change. Fossil evidence is indispensable for studying the distribution of taxa through time, and determining how abiotic parameters shaped ancient biodiversity. Here we report ruminant artiodactyls and a new anthropoid primate from Süngülü, a locality in Eastern Anatolia that has yielded a diversified and largely endemic assemblage of rodents. Three taxa of ruminants are recognized, the tragulid Iberomeryx parvus Gabunia, 1964, a larger species of Iberomeryx Gabunia, 1964, and a bachitheriid referred to cf. Bachitherium sp. A lower molar is identified as the new eosimiid primate Sungulusimias unayae n. gen., n. sp., which is the first occurrence of Paleogene anthropoids in western Asia. The lower molar of Sungulusimias unayae n. gen., n. sp. is characterized by protoconid and metaconid closely spaced and of similar height and volume, paraconid cuspidate and nearly connate with metaconid, strong mesiobuccal cingulid, and entoconid without strong connection to hypoconulid via the postcristid. The composition of this assemblage together with rodents indicates a probable Latest Eocene age for Süngülü, although an early Oligocene age cannot be completely ruled out. The rodent fauna from Süngülü suggests that endemism persisted at the periphery of Balkanatolia until the latest Eocene while Eastern Anatolia was situated in a strategic corridor for faunal exchanges between eastern Asia, Indo-Pakistan and Europe. During the Eocene-Oligocene transition, Balkanatolia probably functioned as a “holding pen” where various taxa were confined for significant intervals of time before proceeding to colonize Western Europe at the Grande Coupure.
Balkanatolia, Ruminantia, anthropoid primate, Eocene-Oligocene transition, new genus, new species