
 Comptes Rendus Palevol
15 (5) - Pages 527-535
Comptes Rendus Palevol
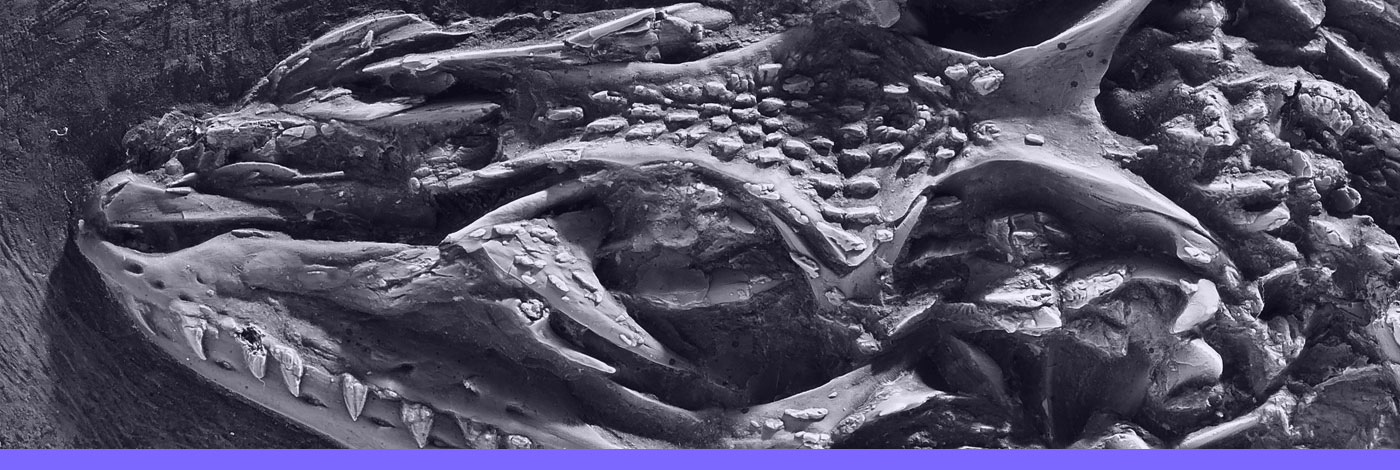
15 (5) - Pages 527-535Through ontogeny, human cranial vault bones undergo differentiation in terms of their shape, size and tissue maturation. This differentiation is visible at both the macroscopic and microscopic levels. Preliminary data from a histological and compartmentalisation exploratory analysis of individuals with different ages suggest differences in the modelling and remodelling patterns through ontogeny. Child vault bones are primarily composed of avascular lamellar bone (largely vascularised), late juvenile or adolescent bones present the largest extension of mineralised areas (highly remodelled) and the lowest vascularisation (diploe is highly reduced), and the adult present highly vascularised bone in which the diploe is again largely extended. During childhood, the existence of an avascular lamellar bone promotes the sealing of the cranium bones surfaces whereas adult vault bones seem to become opened ectocranially due to the remodelling. We discuss the possibility that both effects could be related with the head thermoregulation.
Human cranial bones, Palaeohistology, Compartmentalisation