 Cryptogamie, Algologie
27 (2) - Pages 185-198
Cryptogamie, Algologie
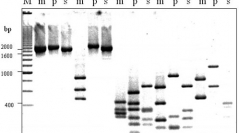
27 (2) - Pages 185-198We used Amplified Ribosomal DNA Restriction Analysis (ARDRA) and sequencing to genetically characterize one Chilean strain of Spirulina (S. subsalsa CONC-050) and two foreign strains of Arthrospira (A. maxima CONC-040 and A. platensis M2). The potential of the strains as a source of the pigment C-phycocyanin (C-PC) was also evaluated. Restriction fragment profiles of the ribosomal internal transcribed spacer (ITS) from A. maxima CONC-040 matched those of the one previously well characterized Arthrospira clade (clade II) of Scheldeman et al. (1999). The ITS sequence of Spirulina was interrupted by the tRNAIle gene while the ITS regions of Arthrospira were interrupted by both tRNAIle and tRNAAla genes. Phylogenetic analysis, including ITS sequences from other strains deposited in GenBank, showed that the ITS region of S. subsalsa CONC-050 is almost identical to the previously sequenced S. subsalsa FACHB351. In relation to the Arthrospira group, A. maxima CONC-040 was reconfirmed as a member of cluster II, while A. platensis M2 was the most divergent and did not group with any other Arthrospira strain. C-PC content was significantly higher in S. subsalsa CONC-050. Antioxidant capacity was evaluated in aqueous extracts containing the same quantity of C-PC. The most protective extract was the one from A. maxima CONC-040, which was the strain that was less productive in terms of C-PC per culture volume.