 Cryptogamie, Bryologie
26 (1) - Pages 49-57
Cryptogamie, Bryologie
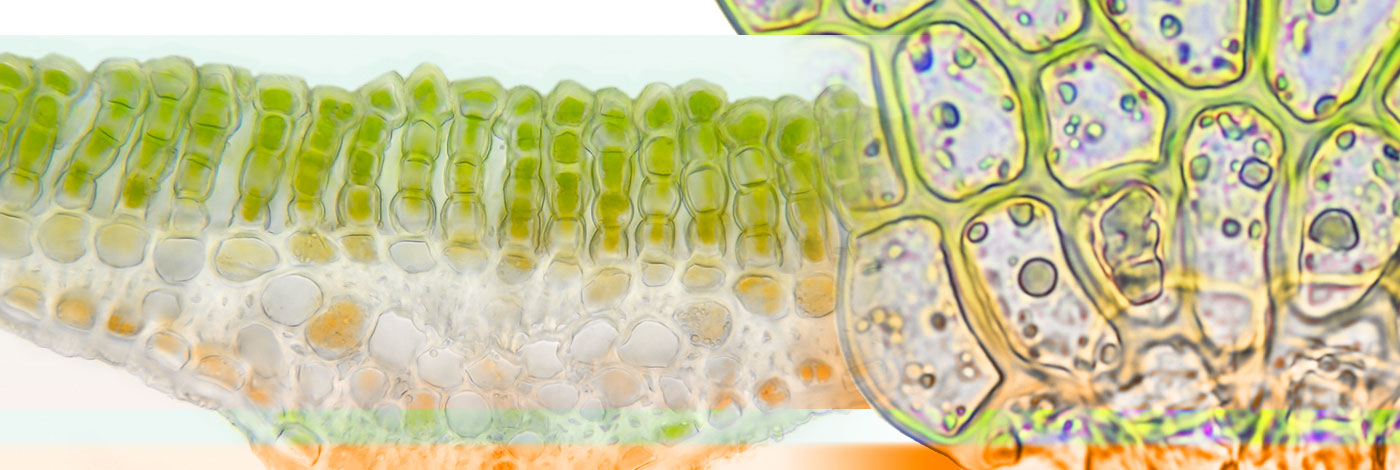
26 (1) - Pages 49-57In recent years, Syzygiella has been alternatively assigned to Plagiochilaceae and Lophoziaceae. Here we use chloroplast gene rbcL sequences to test both hypotheses. Maximum likelihood analyses of an rbcL dataset including 27 species of Jungermanniopsida and Marchantia (Marchantiopsida, outgroup) lead to a topology with two well supported paraphyletic main clades. One main clade comprises Lejeuneaceae in a robust sister relationship with Frullaniaceae and Porellaceae. Syzygiella anomala and S. perfoliata form a well supported monophyletic lineage within the second main clade.They are placed sister to a robust clade made up of Scapania (Scapaniaceae), Lophozia and Tritomaria (Lophoziaceae) in an unsupported sister relationship. The Lophozia – Tritomaria – Scapania – Syzygiella clade is placed sister to a clade with Jungermannia (Jungermanniaceae), Calypogeia (Calypogeiaceae) and Tylimanthus (Acrobolbaceae). The well supported Plagiochilaceae (represented by Chiastocaulon, Plagiochilion and Plagiochila) form a robust sister relationship with Geocalycaceae made up of Heteroscyphus and Chiloscyphus. The phylogentic analysis provides evidence that Syzygiella is loosely related to Lophoziaceae and Scapaniaceae. A closer relationship of Syzygiella and Plagiochilaceae is not supported by the molecular dataset.