 Cryptogamie, Algologie
37 (3) - Pages 179-198
Cryptogamie, Algologie
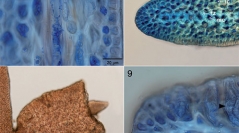
37 (3) - Pages 179-198We analyzed both mitochondrial cox1 and plastid rbcL sequences from specimens of Pterocladiella from Madagascar and compared their morphologies with previously described species in the genus. Both molecular and morphological datasets demonstrated the presence of five species in Madagascar: P. australafricanensis, P. bartlettii, P. caerulescens, and two new species, P. feldmannii and P. hamelii, described here. Pterocladiella feldmannii is distinguished by plants with a size of about 6 cm with narrow axes and opposite to irregular branches, rhizines congested in medulla, tetrasporangial branchlets constricted at base of branches, tetrasporangial sori without sterile margins, and irregular arrangement of tetrasporangia. Pterocladiella hamelii is characterized by plants with a size of about 3 cm with flattened and thin erect axes and irregular branches, radial arrangement of subapical cells at tips of main axes, tetrasporangial sori with sterile margins and horizontal to irregular arrangement of tetrasporangia. Phylogenetic analyses based on cox1 and rbcL sequences revealed the sister relationship between P. feldmannii and P. hamelii, and their distant relationships to P. australafricanensis, P. bartlettii, and P. caerulescens. The Madagascan Pterocladiella is composed of two geographical elements: Madagascan endemic (P. feldmannii and P. hamelii) and species with wide distributions (P. australafricanensis, P. bartlettii and P. caerulescens).